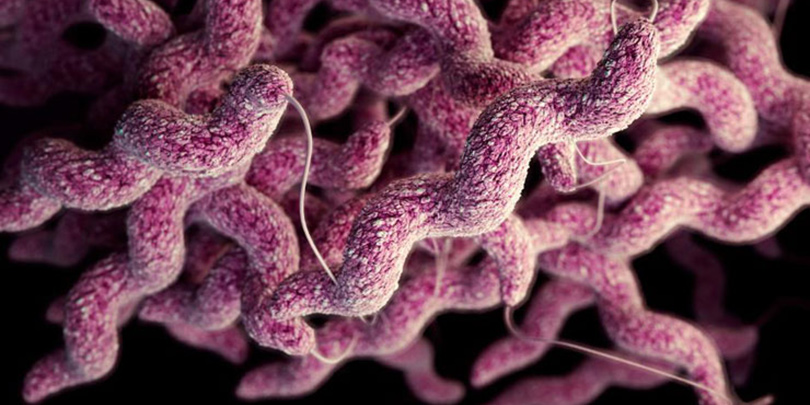
Campylobacter
Key facts
- Campylobacter is a bacteria responsible for intestinal infections.
- Infections with Campylobacter are generally benign, but can be fatal in very young children, the elderly and immunocompromised individuals.
- This bacteria normally colonizes the intestinal tract of warm-blooded animals such as poultry and livestock and is commonly detected in foods derived from these animals..
- The species of the genus Campylobacter can be destroyed by heat and complete cooking of food.
- To prevent infections with Campylobacter care should be taken to follow basic good hygiene practices when preparing food.
The bacteria Campylobacter is a major cause of diarrheal foodborne diseases in humans and the most common bacterial cause of gastroenteritis around the world. In developed and developing countries, it causes more cases of diarrhea that bacteria of the genus Salmonella can be transmitted through food. The high incidence of diarrhea Campylobacter, their duration and their potential effects confer an important socio-economically. In developing countries, infections Campylobacterare particularly common in children under two years, they sometimes cause death.
Genre Campylobacter takes mainly bacteria spiral, S or rounded rods. Currently, it covers 17 species 6 subspecies, including the most commonly reported as the cause of human diseases are C. jejuni (subspecies jejuni) and C. coli. Other species such as C. run and C. upsaliensis have also been isolated from people with diarrhea, but their reporting is less common. Most of these species prefer to grow in a micro-aerobic atmosphere (containing 3 to 10% oxygen). Others tend to favor an anaerobic environment (containing little or no oxygen), even if they are also able to grow in micro-aerobic conditions.
Disease
- Campylobacteriosis is a disease resulting from infection with the bacteria Campylobacter. Symptoms of the disease usually appear two to five days after infection, but the duration of the incubation period can range from one to ten days.
- Among the most common clinical symptoms of infections Campylobacter, include diarrhea (often with bloody stools), abdominal pain, fever, headaches, nausea and / or vomiting. These symptoms usually last between three and six days.
- Deaths from campylobacteriosis are rare and usually concern only the very young and the elderly, or people already suffering from other serious diseases like AIDS.
- Complications such as bacteremia (presence of bacteria in the blood), hepatitis or pancreatitis (infections of the liver and pancreas respectively) and miscarriages have been reported with varying degrees of frequency. There may also be post-infection complications : reactive arthritis (painful joint inflammation that can last several months) and neurological disorders such as Guillain-Barré syndrome, a form of paralysis offering similarities poliomyelitis and may result in severe respiratory and neurological dysfunctions, or death in a few cases.
Sources and transmission
The species of the genus Campylobacter are found in most warm-blooded animals. They are present in animals intended for human food such as poultry., cattle, pigs, sheep, ostriches and shellfish, and in pets such as dogs and cats.
It is generally believed that the main route of transmission is through food and through the consumption of undercooked meat and meat products or even raw or contaminated milk.. Contaminated water or ice are also sources of infection. A certain proportion of cases result from contact with contaminated water during recreational activities.
Campylobacteriosis is a zoonosis, that is to say a disease transmitted to humans by animals or animal products. Most of the time, carcasses or meat are contaminated Campylobacter by feces during slaughter. It is rare that this bacteria causes disease in animals.
The relative contribution of each of the sources mentioned above to the global burden of disease is not clearly known, but it is thought that contaminated and undercooked poultry meat consumption is a major contribution. As outbreaks with a common source rather cover a small proportion of cases, the vast majority of reports involve sporadic cases, no easily discernable pattern. Estimate the importance of all known sources is extremely difficult also, the fact that Campylobacter is extremely widespread also hinders the development of control strategies covering the entire food chain. However, in countries that have implemented specific strategies to reduce the prevalence of this bacteria in live poultry, a similar reduction in the frequency of human cases is observed.
Treatment
Treatment is usually unnecessary, except electrolyte replacement and rehydration. Antimicrobial treatment (erythromycin, tetracycline, quinolones) is recommended in invasive cases (when the bacteria invades the cells of the intestinal lining and damages the tissues) or to eliminate healthy carriers (individuals who host Campylobacter in their organization and continue to excrete while remaining asymptomatic).
Prevention methods
- Prevention is based on the implementation of measures at all stages of the food chain, of agricultural production at a farm processing, in the manufacture and preparation of food in industrial or domestic environment.
- In countries without adequate systems of sewage disposal, faeces and all objects contaminated by such materials must be disinfected before disposal.
- Measures to reduce the prevalence of Campylobacter in poultry include strengthening biosecurity to prevent transmission of this bacteria from the environment to flocks of birds on farms. This option to combat infection is only feasible if the birds are kept in a closed environment..
- Good hygienic slaughter practices reduce contamination of carcasses with faeces, but do not guarantee the absence of Campylobacter in meat and derived products. Educating employees in slaughterhouses and raw meat production plants on hygienic food handling is essential to keep contamination to a minimum..
- Methods for controlling infection in home kitchens are similar to those for other foodborne bacterial illnesses.
- Bactericidal treatments such as heating (cooking or pasteurization, for example) or irradiation are the only effective methods to eliminate Campylobacter contaminated food.
Recent Posts
Cakes, Candy : Warning on nanoparticles
100 % tested products contained nanoparticles ! [...] Les résultats de cette expérience ont…
How to eliminate toxins ?
After a series of festive meals, caloric menus, alcoholic or carbonated drinks,…
Plastic, not so fantastic!
Plastic pollutes the environment, we all know it. Il faut aussi rappeler que les objets…
How to eat healthy during lunch break ?
At work, lunch breaks are often done on the go, en quelques minutes et…
Eat healthy, it's really possible ?
These last years, le bio et le sain se sont imposés avec insistance dans nos…
Sausages and merguez salmonella
The company L’Atelier du Valois has recalled batches of "Plateau variegated" suite…

